EFNA1 Antibody
-
中文名稱:EFNA1兔多克隆抗體
-
貨號:CSB-PA256498
-
規格:¥1100
-
圖片:
-
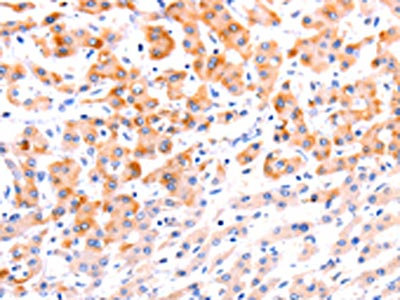
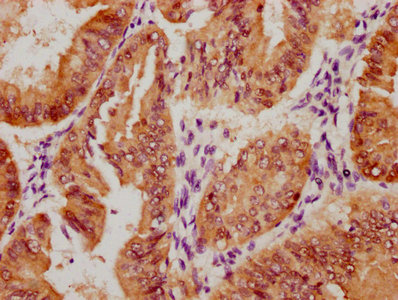
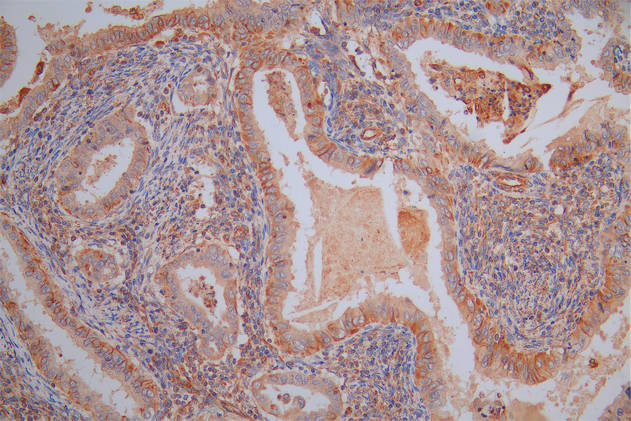
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using CSB-PA256498(EFNA1 Antibody) at dilution 1/37, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
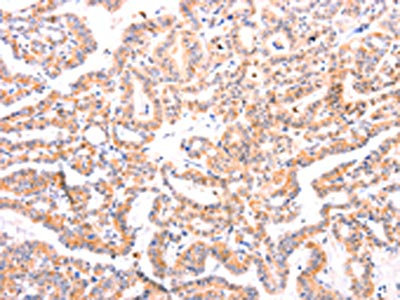
The image on the left is immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human thyroid cancer tissue using CSB-PA256498(EFNA1 Antibody) at dilution 1/37, on the right is treated with fusion protein. (Original magnification: ×200)
-
-
其他:
產品詳情
-
Uniprot No.:
-
基因名:
-
別名:B61 antibody; ECKLG antibody; EFL 1 antibody; EFL1 antibody; EFNA 1 antibody; Efna1 antibody; EFNA1_HUMAN antibody; EPH related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 1 antibody; EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinase ligand 1 antibody; Ephrin-A1 antibody; Ephrin-A1, secreted form antibody; EphrinA1 antibody; EPLG 1 antibody; EPLG1 antibody; Immediate early response protein B61 antibody; LERK 1 antibody; LERK-1 antibody; LERK1 antibody; Ligand of eph related kinase 1 antibody; OTTHUMP00000033242 antibody; OTTHUMP00000033271 antibody; secreted form antibody; TNF alpha-induced protein 4 antibody; TNFAIP 4 antibody; TNFAIP4 antibody; Tumor necrosis factor alpha induced protein 4 antibody; Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 4 antibody
-
宿主:Rabbit
-
反應種屬:Human,Mouse,Rat
-
免疫原:Fusion protein of Human EFNA1
-
免疫原種屬:Homo sapiens (Human)
-
標記方式:Non-conjugated
-
抗體亞型:IgG
-
純化方式:Antigen affinity purification
-
濃度:It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
-
保存緩沖液:-20°C, pH7.4 PBS, 0.05% NaN3, 40% Glycerol
-
產品提供形式:Liquid
-
應用范圍:ELISA,IHC
-
推薦稀釋比:
Application Recommended Dilution ELISA 1:1000-1:5000 IHC 1:50-1:150 -
Protocols:
-
儲存條件:Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
-
貨期:Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
-
用途:For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Cell surface GPI-bound ligand for Eph receptors, a family of receptor tyrosine kinases which are crucial for migration, repulsion and adhesion during neuronal, vascular and epithelial development. Binds promiscuously Eph receptors residing on adjacent cells, leading to contact-dependent bidirectional signaling into neighboring cells. Plays an important role in angiogenesis and tumor neovascularization. The recruitment of VAV2, VAV3 and PI3-kinase p85 subunit by phosphorylated EPHA2 is critical for EFNA1-induced RAC1 GTPase activation and vascular endothelial cell migration and assembly. Exerts anti-oncogenic effects in tumor cells through activation and down-regulation of EPHA2. Activates EPHA2 by inducing tyrosine phosphorylation which leads to its internalization and degradation. Acts as a negative regulator in the tumorigenesis of gliomas by down-regulating EPHA2 and FAK. Can evoke collapse of embryonic neuronal growth cone and regulates dendritic spine morphogenesis.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- ephrin-A1 seems to be remarkably involved in elementary processes of endothelial migration like cellular polarization, migratory direction and speed. PMID: 27742560
- Findings show that EFNA1 expression is a useful marker for predicting a high risk of recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients but not EPHA2. PMID: 24969670
- Results suggest that EFNA1 is involved in colorectal tumorigenesis, and rs12904 A>G polymorphism in the 3' UTR of EFNA1 is associated with CRC susceptibility in a Chinese population. PMID: 24175772
- EphA2-ephrinA1 trans-endocytosis is sensitive to the mechanical properties of a cell's microenvironment PMID: 24853748
- Ephrin-A1 is upregulated in tumor microenvironment and promotes angiogenesis through a coordinated cross-talk with PI3K/Akt-dependent eNOS activation. PMID: 24040255
- The interaction between ephrin-As, Eph receptors and integrin alpha3 is plausibly important for the crosstalk between Eph and integrin signalling pathways at the membrane protrusions and in the migration of brain cancer cells. PMID: 23686814
- Increased expression of EFNA1 mRNA is associated with gastric cancer. PMID: 23065816
- Expression of EPHRIN-A1 tends to be associated with worse survival in head and neck cancer. PMID: 24330498
- EFNA1 expression is a useful marker for predicting high risk of relapse and cancer-related death in patients who have undergone curative resection for CRC. PMID: 23258614
- Findings suggest that the glycosylation on ephrin-A1 plays a critical role in the binding and activation of the EphA2 receptor. PMID: 23661698
- present study showed a high expression of EphA2/ephrinA1 in adenoid cystic carcinoma. EphA2/ephrinA1 can serve as a novel therapy target for adenoid cystic carcinoma. PMID: 23298804
- EphA2 activation by ephrin-A1 induces tumor suppressor gene cdx-2 expression which attenuates cell proliferation, tumor growth and thus may be a promising therapeutic target against NSCLC. PMID: 22824143
- in p-stage I NSCLC patients, those in the higher EphA2 expression and higher ephrin-A1 expression groups shared almost the same clinicopathological backgrounds which are generally considered to be better prognostic factors. PMID: 22236865
- The EphA2 ligand EphrinA1 induces EphA2 phosphorylation and intracellular internalization and degradation, thus inhibiting breast tumor progression. PMID: 22228563
- Multiple oncogenic signalling pathways are affected by ephrin-A1, from the promotion of a specific pathway in one cell or cancer type to the inhibition of the same pathway in another type of cell or cancer. [Review] PMID: 22040911
- Ovarian serous carcinomas and ovarian cancer cell lines overexpress EphA2 and EphrinA-1. Tumor patients with higher expression levels of both EphA2 and EphrinA-1 have a significantly poorer clinical outcome. PMID: 21500549
- The Eph-ephrinA system can promote cell attachment along with intercellular dissociation. PMID: 21349856
- This study demonstrated that the Eph-ephrin A system can promote intercellular dissociation in Ishikawa cells suggesting an important role in the initial step of embryo implantation by opening the endometrial epithelial cell barrier. PMID: 21138904
- Osteosarcoma samples were characterized using genome-wide microarrays: increased expression of the EphA2 receptor and its ligand EFNA1 was detected. PMID: 21166698
- up-regulation of EphA2 and down-regulation of Ephrina1 may correlate with poor prognosis for patients with high-grade glioma PMID: 20571968
- EphA2 and EphrinA1 are highly expressed in renal cell carcinoma, and positively correlated with histological differentiation, clinical stage and angiogenesis. PMID: 19950554
- EFNA1 may be a useful serum marker for the detection of hepatocellular carinoma development and progression. PMID: 19642143
- The interaction between EphA2 and this ligand protein is necessary for induction of maximal neovascularization by VEGF. PMID: 12496364
- This protein, an EphA ligand, stimulated protein degradation by EphA2. PMID: 12496371
- Ephrin-A1 stimulation of Jurkat T cells induces tyrosine phosphorylation of EphA3 receptors and cytoplasmic proteins, including c-cbl proto-oncogene, and causes down-regulation of endogenous EphA3 receptors from the cell surface and their degradation. PMID: 12794130
- A new ephrin-A1 isoform, ephrin-A1b, lacks a segment of 22 amino acids (residues 131-152). Exon 3 is spliced out in its transcript. It may regulate the function of its ephrin-A1a counterpart. PMID: 14692877
- This study demonstrates for the first time significantly reduced ephrin-A1 expression in T cells of asthma patients. PMID: 14707054
- found ephrin-A1 expressed exclusively in the invasive extravillous trophoblast in preeclampsia and normal placenta PMID: 15193868
- ephrin-A1 is expressed by venule endothelial cells PMID: 15585656
- EPHA2 and EFNA1 expression may influence the behavior of human gastric cancer. PMID: 15649254
- low molecular weight protein-tyrosine phosphatase acts as terminator of EphA2 signaling causing efficient negative feedback loop on biological response mediated by ephrinA1; tyrosine phosphorylation main event orchestrating repulsive response PMID: 16051609
- High expression of Ephrin A-1 is associated with urinary bladder carcinoma. PMID: 16428472
- Activation of ERK-1/2 plays an essential role in ephrin-A1-mediated cell migration, whixh is inhibited by green tea catechin epigallocatechin gallate. PMID: 17049832
- Ephrin-A1 serves as a critical negative regulator in the tumorigenesis of gliomas by down-regulating EphA2 and FAK. PMID: 17332925
- Increasing ephrin-A expression enhances T-cell interactions not only with purified integrin ligands but also endothelial cells, while EphA activation down-regulates these interactions. PMID: 17980912
- Soluble monmomeric EphrinA1 is released from tumor cells and is a functional ligand for the EphA2 receptor. PMID: 18794797
- The function of EphA2 and ephrinA1 in tumorigenesis and tumor progression is complex and seems to be dependent on cell type and microenvironment PMID: 19074825
- Increased expression of EphA2 and EphrinA-1 plays an important role in the progression human gastric adenocarcinoma. PMID: 19101799
- The crystal structures of an A-class complex between EphA2 and ephrin-A1 and of unbound EphA2, are presented. PMID: 19525919
顯示更多
收起更多
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor, GPI-anchor.; [Ephrin-A1, secreted form]: Secreted.
-
蛋白家族:Ephrin family
-
組織特異性:Brain. Down-regulated in primary glioma tissues compared to the normal tissues. The soluble monomeric form is expressed in the glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) and breast cancer cells (at protein level).
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
-
YWHAB Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, FC
Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
-
Phospho-YAP1 (S127) Recombinant Monoclonal Antibody
Applications: ELISA, WB, IHC
Species Reactivity: Human
-
-
-
-
-