產品詳情
-
產品描述:小鼠凋亡相關因子(FAS/CD95)酶聯免疫試劑盒(CSB-E04543m)為雙抗夾心法ELISA試劑盒,定量檢測血清、血漿、組織培養上清液、組織勻漿樣本中的FAS含量。FAS是重要的細胞表面受體。其背景上,在細胞凋亡調控等生理過程中意義重大。研究機制方面,FAS與配體結合后,會激活級聯反應,誘導細胞凋亡,在腫瘤、自身免疫病等疾病研究里,是潛在治療靶點。試劑盒檢測范圍為0.625 ng/mL-40 ng/mL,適用于體外細胞凋亡機制研究、藥物干預效果評估或動物模型中FAS信號通路的動態監測,為探索細胞程序性死亡調控機制、免疫微環境分析及靶向治療開發提供可靠工具本品僅用于科研,不用于臨床診斷,產品具體參數及操作步驟詳見產品說明書。
-
別名:Fas; Apt1; Tnfrsf6; Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6; Apo-1 antigen; Apoptosis-mediating surface antigen FAS; FASLG receptor; CD antigen CD95
-
縮寫:
-
Uniprot No.:
-
種屬:Mus musculus (Mouse)
-
樣本類型:serum, plasma, cell culture supernates, tissue homogenates
-
檢測范圍:15.6 pg/mL-1000 pg/mL
-
靈敏度:3.9 pg/mL
-
反應時間:1-5h
-
樣本體積:50-100ul
-
檢測波長:450 nm
-
研究領域:Cell Biology
-
測定原理:quantitative
-
測定方法:Sandwich
-
精密度:
Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. -
線性度:
To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse FAS in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. Sample Serum(n=4) 1:1 Average % 104 Range % 97-108 1:2 Average % 106 Range % 97-110 1:4 Average % 94 Range % 85-97 1:8 Average % 100 Range % 92-104 -
回收率:
The recovery of mouse FAS spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. Sample Type Average % Recovery Range Serum (n=5) 103 95-107 EDTA plasma (n=4) 100 89-104 -
標準曲線:
These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. 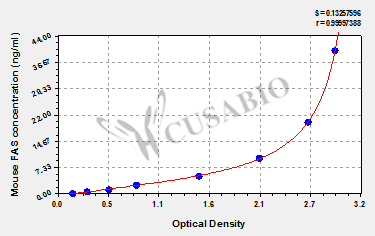
ng/ml OD1 OD2 Average Corrected 40 2.965 2.848 2.907 2.737 20 2.658 2.592 2.625 2.455 10 2.166 2.079 2.123 1.953 5 1.502 1.478 1.490 1.320 2.5 0.832 0.844 0.838 0.668 1.25 0.551 0.543 0.547 0.377 0.625 0.329 0.319 0.324 0.154 0 0.172 0.168 0.170 -
數據處理:
-
貨期:3-5 working days
引用文獻
- Modulating flavanone compound for reducing the bitterness and improving dietary fiber, physicochemical properties, and anti-adipogenesis of green yuzu powder by enzymatic hydrolysis HJ Seong,Food chemistry,2024
- Killing Effects of IFN R-/- Mouse NK Cells Activated by HN Protein of NDV on Mouse Hepatoma Cells and Possible Mechanism with Syk and NF-kappaB Liang S,ANATOMICAL RECORD-ADVANCES IN INTEGRATIVE ANATOMY AND EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY,2019
- Killing Effects of IFN R-/- Mouse NK Cells Activated by HN Protein of NDV on Mouse Hepatoma Cells and Possible Mechanism with Syk and NF-kappaB Liang S,ANATOMICAL RECORD-ADVANCES IN INTEGRATIVE ANATOMY AND EVOLUTIONARY BIOLOGY,2019
相關產品
靶點詳情
-
功能:Receptor for TNFSF6/FASLG. The adapter molecule FADD recruits caspase-8 to the activated receptor. The resulting death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) performs caspase-8 proteolytic activation which initiates the subsequent cascade of caspases (aspartate-specific cysteine proteases) mediating apoptosis. FAS-mediated apoptosis may have a role in the induction of peripheral tolerance, in the antigen-stimulated suicide of mature T-cells, or both.
-
基因功能參考文獻:
- our computational and experimental approach identified Fas as a regulator of the Th17-to-Th1 cell balance by controlling the availability of opposing STAT1 and STAT3 to have a direct impact on autoimmunity. PMID: 29562202
- FGF21 alleviated atherosclerosis by ameliorating Fas-mediated apoptosis in apoE-/- mice. PMID: 30157856
- TPD7 altered the extrinsic apoptosis pathway by upregulating Fas expression. PMID: 29901176
- In conclusion, these data demonstrate that murine herpesvirus 68-immortalized SL-1 cells can be recognized and controlled by specific cytotoxic T cells through CD95/CD95L-mediated apoptosis. PMID: 28516317
- Findings indicate that induction of apoptosis through Fas is dependent on receptor palmitoylation in primary immune cells, and Fas may prevent autoimmunity by mechanisms other than inducing apoptosis. PMID: 28008916
- Both Sharpin/Fas and Sharpin/Fasl compound mutant mice developed an auto-inflammatory phenotype similar to that seen in Sharpin null mice, indicating that initiation of apoptosis by FAS signalling is likely not involved in the pathogenesis of this disease. PMID: 28094869
- Tag7 activates lymphocytes capable of Fasl-Fas-dependent contact killing of virus-infected cells. PMID: 29083508
- leucine deprivation induces the expression of miR-212-5p in a GCN2/ATF4-dependent manner. miR-212-5p suppresses lipid accumulation in liver by targeting FAS and SCD1 under both normal diet and high-fat diet conditions. PMID: 28667176
- Our data show that loss of Fas activity strongly affects the early development of atopic dermatitis (AD) by leading to Th2-dominant inflammation characterized by dermal infiltration of CD4+ T cells, neutrophils and increased skin expression of Th2 cytokines.However, Fas/FasL-apoptotic pathway is also involved in restricting tissue remodelling and dermal fibrosis during AD. PMID: 28434120
- Hrd1-null B cells exhibited high Fas expression during activation and rapidly underwent Fas-mediated apoptosis, which could be largely inhibited by FasL neutralization. Fas mutation in Hrd1 KO mice abrogated the increase in B-cell AICD. We identified Hrd1 as the first E3 ubiquitin ligase of the death receptor Fas and Hrd1-mediated Fas destruction as a molecular mechanism in regulating B-cell immunity. PMID: 27573825
- FAS contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction, steatosis development, and insulin resistance under high fat diet. PMID: 28883393
- These findings reveal a role for MOAP-1 in Fas signaling in the liver by promoting MTCH2-mediated tBid recruitment to mitochondria. PMID: 27320914
- The in vivo delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 could maintain liver homeostasis and protect hepatocytes from Fas-mediated cell apoptosis in the fulminant hepatic failure model. PMID: 27585307
- This study demonstrated that Ischemic neurons release sFasL, which contributes to M1-microglial polarization. PMID: 27283206
- results indicate that IL-1beta, produced by the inflammasome and Fas-dependent mechanisms, contributes cooperatively to the Th17/Th1 induction during bacterial infection. This study provides a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying Th17/Th1 induction during pathogenic microbial infections in vivo. PMID: 28674179
- this study shows that CD95-mediated calcium signaling promotes Th17 cell trafficking to inflamed organs in lupus-prone mice PMID: 27438772
- accelerating effects of Tlr9 deficiency PMID: 28278279
- K8/K18-dependent PKCdelta- and ASMase-mediated modulation of lipid raft size can explain the more prominent FasR-mediated signaling resulting from K8/K18 loss. PMID: 27422101
- Data show that TCF1 proteindeficiency relieved most manifestations of autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS)-like phenotype, which were caused by Fas protein mutation in TCF1(-/-) lpr/lpr mice. PMID: 28349581
- Results indicate that the close interaction between Thy-1 and Fas in lipid rafts regulates fibroblast apoptosis, and decreased fibroblast apoptosis associated with myofibroblast accumulation in mice lacking Thy-1. PMID: 28165468
- Fas/FasL Complex Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Brain Endothelial Cells Via FADD-FLIP-TRAF-NF-kappaB Pathway PMID: 25427888
- Cardiac Fas-dependent and mitochondria-dependent apoptotic pathways were activated in transgenic mice with Huntington's disease. PMID: 25800750
- The MWM showed that compared with FAS- and FASL-knockout mice treated with sevoflurane, sevoflurane treatment of wild-type mice significantly prolonged the escape latency and reduced platform crossing times. PMID: 26782453
- the individual functions of the NF-kappaB family members NF-kappaB1, NF-kappaB2 and c-REL in the various autoimmune pathologies of Fas(lpr/lpr) mutant mice, were investigated. PMID: 26084385
- When Bax(-/-)Bak(-/-) murine embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are stimulated to differentiate, a subpopulation fails to do so and instead upregulates FAS in a p53-dependent manner to trigger Bax/Bak-dependent apoptosis. PMID: 26585277
- These results demonstrate that during ectromelia virus infection, Fas/FasL can regulate development of tolerogenic DCs and Tregs, leading to an ineffective immune response. PMID: 26780774
- Data determined the transmembrane domain structure of Fas and showed that the trimer assembly, which is mediated by a proline-containing motif, is essential for Fas signaling providing structural explanation for many known cancer mutations in this domain. PMID: 26853147
- Impaired Fas-Fas Ligand Interactions Result in Greater Recurrent Herpetic Stromal Keratitis in Mice PMID: 26504854
- miR-150 deficiency prevents Fas-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury through regulation of the Akt pathway PMID: 26196694
- CD47 deficiency ameliorates lupus nephritis in Fas(lpr) mice via suppression of IgG autoantibody production. PMID: 26095930
- The upregulation of p-FADD/FADD ratio and NF-kappaB in mouse hippocampus after Kainic acid treatment PMID: 26044520
- demonstrates that Fas/FasL pathway during ectromelia virus infection of the lungs plays an important role in controlling local inflammatory response and mounting of antiviral response PMID: 25873756
- Mice with the Fas(lpr) gene developed severe systemic lupus erythematosus with renal dysfunction and inflammatory responses in the lung and kidney. By contrast, mice with the Fas(+) gene showed disease-related abnormalities in the liver and joints. PMID: 25941813
- Occlusive lung arterial lesions triggering pulmonary arterial hypertension developed in a new model of endothelial-targeted, Fas-induced apoptosis transgenic mice. PMID: 25879383
- Gene silencing of liver Fas expression completely attenuated apoptotic and necrotic cell death. PMID: 25601293
- Our results demonstrate that Fas/FasL can regulate development of tolerogenic dendritic cells and expansion of Tregs early during HSV-2 infection, which further influences effective anti-viral response. PMID: 25129477
- our data support a model in which IFNgamma- and Fas/FasL-dependent activation of intratumoral Mvarphis by CD8(+) T cells promotes severe intraocular inflammation that indirectly eliminates intraocular tumors by inducing phthisis. PMID: 25248763
- Meningococcal capsular polysaccharide-loaded vaccine nanoparticles induce expression of CD95. PMID: 24981893
- These data provide the first in vivo genetic evidence that neutrophil lifespan is controlled by death receptor signaling and provide a mechanism to account for neutrophil resistance to Fas stimulation during infection. PMID: 25473101
- Intestinal expression of Fas and Fas ligand is upregulated by bacterial signaling through TLR4 and TLR5, with activation of Fas modulating intestinal TLR-mediated inflammation. PMID: 25378591
- overexpression of Fas/FasL is associated with infectious complications and severity of experimental severe acute pancreatitis by promoting apoptosis of lymphocytes PMID: 24566874
- No significant association between FAS-670G/A polymorphism and susceptibility to autoimmune hepatitis was found. PMID: 24629822
- a key role of MK2 and FasR in the regulation and limitation of the immune response in the CNS PMID: 24964076
- These data show that loss of Fas activity specifically in chondrocytes prolonged the life span of chondrocytes and that Fas synergized with TNFalpha signaling to mediate chondrocyte apoptosis. PMID: 24677136
- Although expression of Fas and TNF-R1 was proportionate to fractional apoptosis, cell death was dominated by spontaneous apoptosis in stem cell mobilization. PMID: 24566711
- Data suggest that toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), survivin, Fas ligand (FasL), and CD95 (Fas) genes are involved in the development of cervical cancer. PMID: 25106857
- The Fas KO mice spontaneously develop blepharitis with not only autoimmune inflammation with deposition of auto-antibody but also allergic inflammation with infiltration by eosinophils and show to increase serum level of IgE and IgG1. PMID: 23220580
- D-cyclins repress the expression of the death receptor Fas and its ligand, FasL PMID: 25087893
- Data indicate that dendritic cells (DCs)-specific CD95 (Fas) expression plays a role in regulation of antiviral responses and suggests a strategy for stimulation of T cells for virus clearance in chronically infected animal and human. PMID: 24912151
- Combined adenovirus-mediated artificial microRNAs targeting mfgl2, mFas, and mTNFR1 protect against fulminant hepatic failure in mice. PMID: 24303082
顯示更多
收起更多
-
相關疾病:Defects in Fas are the cause of the lymphoproliferation phenotype (lpr). Lpr mice show lymphadenopathy and autoantibody production.
-
亞細胞定位:Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane raft.
-
組織特異性:Detected in various tissues including thymus, liver, lung, heart, and adult ovary.
-
數據庫鏈接:
Most popular with customers
-
Human Transforming Growth factor β1,TGF-β1 ELISA kit
Detect Range: 23.5 pg/ml-1500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 5.8 pg/ml
-
-
-
Mouse Tumor necrosis factor α,TNF-α ELISA Kit
Detect Range: 7.8 pg/ml-500 pg/ml
Sensitivity: 1.95 pg/ml
-
-
-
-